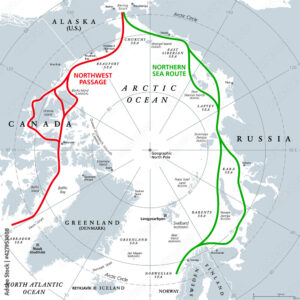
For forty years I tried to look at Logistics as a Strategic asset and wrote quite 400 articles to give to top managers the feeling of the importance of what they thought only regarding warehouses and cost of transport to minimise. Now with war, supply chain disruption and enormous Chinese investments on the new silk ways, someone start to understand that Logistics is a key for success of Strategy, not vice versa. And Climate Change is another powerful factor to focus new ideas and new routes, which will revolutionise the logistic world. In 2000 I was in Kirkenes, north of Norway, during tragedy of Russian atomic submarine Kursk, and they were already discussing about future North East passage. but just like an utopia. Now everything changed, 50 Russian icebreaker, half of them atomic, keep opened the route to quite 30 million tons of goods flowing from China to Europe, about 5% to 10% of total traffic, difficult to estimate because of large variety of goods mix changing , which reached a value of 400 billion $/year, quite the world export of Italy. The North West passage along Canadian coasts, remained until now to experimental stage , tested from some Chinese ships but not relevant as the North East. Geopolitical conflict between USA and Canada for the governance of the route, lower investments in ports and service infrastructure compared to Russian ones, all these factors are retarding the opening of this route, historically the most famous in the past marine literature.
These new routes are not easily performed, and a lot of work remain to do ,but the future seems clear in favour of this new logistic, and human, space. For ten years Russia was preparing the governance of North East route, where it has the longest coasts rim on Arctic sea. Russia developed several major ports that are located in the Arctic region and are designed to support shipping along the Northern Sea Route (NSR),the other denomination of North east passage. These ports are strategically located along the NSR and provide key infrastructure for international shipping between Europe and Asia. Some of the major Arctic ports in Russia include:
Murmansk – Murmansk is the largest port in the Russian Arctic and is well-equipped to handle cargo throughout the year. It is situated on the Kola Bay in the Barents Sea.
Dudinka – Dudinka is located on the Yenisei River in the Taymyr Peninsula and is a major hub for the export of raw materials, including coal, oil, and gas. The other port in the area is Dikson.
Arkhangelsk – Arkhangelsk is located at the junction of the Northern Dvina and the White Sea and serves as a crucial gateway to the NSR.
Sabetta is a new deep-water port on the Yamal Peninsula that is designed to accommodate LNG carriers and support the production and export of liquified natural gas.
Pevek – Pevek is located on the East Siberian Sea and serves as a key transportation hub for goods and raw materials from the Chukotka Autonomous Okrug region.
Investments in ice breakers have also been determinant to assure the maintenance of an open passage and to pilot long convoys of ships crossing the route. The projected time sparing of 10 to 15 days of navigation in front of Suez channel, in practice is not completely performed because of ice and weather conditions slowing navigation. Other major costs regard needs of food and spare parts support due to minor land assistance and personnel cost for the special difficult operative conditions on board, and of course the ice breaker operations. So the discussion about convenience in front of Suez remain open, but all the geopolitical factors are favourable for China, starting from bypassing India and Malaysia, western control points from British empire, to the Middle East permanent political turmoil, to operational cost of Mediterranean ports. Laissez faire, laissez passer remains valid especially in Logistics and Commercial empires building.