Seven centuries after the battle of iced Peipus lake between Estonia and Russia(1242),where Alexander Nevskij led to victory Russian tribes against Teutonic Order, let’s go to resume main geopolitical fractures in this Baltic area, so strategical for Europe. In the last fifteen years Baltic area development has been very impressive. Not only in the northern rim are the most rich and socially developed countries of the world, Norway, Sweden and Finland, but also the southern rim, coasts from Denmark to West Germany, as those of East Germany, Poland, Lithuania, Latvia, Estonia and the Russian Federation, performed very brilliantly and grew at high rate of GDP development and society changing speed. Whereas the Mediterranean world is very unbalanced and with poor performances both economical, civil and cultural, Baltic sea drives the European way to globalisation and their population are converging toward more balanced situation along all the coasts and castles (37) remembering a glorious past. Cities like Rostock,Schwerin, Riga, Vilnius,and of course the already famous Sankt Petersburg, are now internationally famous and attractive for tourists and businessmen, quite like Copenhagen, Hamburg or Stockholm.
Seven centuries after the battle of iced Peipus lake between Estonia and Russia(1242),where Alexander Nevskij led to victory Russian tribes against Teutonic Order, let’s go to resume main geopolitical fractures in this Baltic area, so strategical for Europe. In the last fifteen years Baltic area development has been very impressive. Not only in the northern rim are the most rich and socially developed countries of the world, Norway, Sweden and Finland, but also the southern rim, coasts from Denmark to West Germany, as those of East Germany, Poland, Lithuania, Latvia, Estonia and the Russian Federation, performed very brilliantly and grew at high rate of GDP development and society changing speed. Whereas the Mediterranean world is very unbalanced and with poor performances both economical, civil and cultural, Baltic sea drives the European way to globalisation and their population are converging toward more balanced situation along all the coasts and castles (37) remembering a glorious past. Cities like Rostock,Schwerin, Riga, Vilnius,and of course the already famous Sankt Petersburg, are now internationally famous and attractive for tourists and businessmen, quite like Copenhagen, Hamburg or Stockholm.
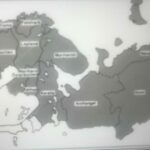
Notwithstanding these nice perspectives, deep fractures lines run under the quiet surface of Baltic sea, coming from a long history of conflicts and from different geopolitical views of the main countries having different interests in the area. One million people in Riga waiting the first visit of a USA president in may 2005 demonstrated the basic trust in America and the surviving of cultural worries inherited from the past.The main regional powers active in the area are Russia, Poland, Sweden and Germany(UE). After the collapse of Soviet Union in Baltic states in 1989 northern rim moved to southern rim along traditional cultural and geopolitical influence areas. So Finland dedicated investments to Estonia, technological leader of the region, where Skype was invented and digitalisation has the most diffusion of the world in every activity. Sweden focused its effort on Latvia, attracted by its forest, its financial system, the shipping line Riga-Stockholm (Stockholm business school is in Riga). Poland historically was naturally linked to Lithuania. Germany has been the great absent, considering the colonisation of these areas from Teutonic Orders during the north crusade of Innocenzo III in 1200, the occupation during the second world war, the annexing of Memel today Klaipeda in Lithuania, the Prussia traditions in Konigsberg, today Russian Kaliningrad. Along the silent economical influence of Scandinavian powers from 1990, Russia and Poland were growing their influence in the following decades, according to their internal economic situation improvement. Minorities of Russian in Estonia and Latvia, around 20% of population started to ask more rights of using their language and Latvia took a referendum on this two years ago, with one region on five saying “yes” for bilinguism. The same 8% Polish in Lithuania asking for more rights. On the lake of historical battle, now you can see Mig flying reaffirming that these countries were the garden of the czars from Sankt Petersburg, The big Rundale castle in Latvia was a gift ordered to Italian architect Rastrelli from Catrine I to her german tutor and lover von Biron.
The main strategic axis to Europe is for Russia the Moscow-Minsk-Varsawa line, but in Baltic states, declared independent in 1918 by Lenin, there are memories and real estate and financial interests rooted in a long common history. The new governments after 1989 runned toward Europe but also with more energy to OTAN to look for protection from Russian bear. Of course the minorities rights have been denied for revenge of Soviet times, but these minorities can’t return to Russia, so a solution similar to North/South Tyrol should be studied, otherwise this fracture will continue to operate. And consequently acts the Sweden/Russian fracture, with deep geopolitical roots and Sweden financial system gaining position in Latvia. More subtle, mainly cultural but very present is the slavish/mongol divide regarding Finland and Estonia, being these countries a innovation model highly competitive for Europe and Russia. On the same basis of conflict with Russia, Poland will push from the back with its traditional anti-Russia policy. Lithuania and Poland troops were along Moscow streets any moment, like Mongols from East, in the middle age until Ivan IV expansion to west and east.
This area continues to grow because of entrepreneurship and culture of its populations, because of mutual fertilisation of northern and southern rim of Baltic sea, because of the favourable perspectives of new euroasiatica infrastructure and the Artic route, but a strict attention to these fractures we summarised here in few words should be provided by some international power, could be also an UE not so bureaucratic, like it was USA once. Could be also Germany which until now demonstrated a strategic vacuum in its policy. In any case should be created a local Council trying to mediate on all these underground tensions, otherwise they will explode again like in the past. We were very confident in Jugoslavia and then exploded, in Czechoslovakia and then splitted. Geopolitical background can be overcome but in centuries not in fifty years. Baltic area more than others European complex situation must be carefully studied, understood, helped. Always taking into account geopolitic vision and cross-cultural analysis.